Micro-Credentials in 2025: US Job Market Impact Analysis

Anúncios
Micro-credentials are poised to redefine the 2025 US job market by providing targeted, verifiable skills that bridge talent gaps and empower individuals for rapid career advancement in a dynamic economy.
Anúncios
The landscape of professional development is shifting dramatically. As we approach 2025, the role of micro-credentials in 2025’s US job market: a comprehensive analysis reveals a profound transformation in how skills are acquired, validated, and valued. Are traditional degrees still enough, or are these bite-sized certifications becoming the new gold standard for career growth?
The Rise of Micro-Credentials: A New Educational Paradigm
Micro-credentials represent a significant departure from traditional education. They are concentrated, verifiable units of learning that certify specific skills or competencies, often taking less time and costing less than a full degree. This shift is driven by the rapid pace of technological change and the increasing demand for specialized skills in the workforce.
Anúncios
In the US, employers are increasingly seeking candidates with demonstrable, up-to-date skills rather than just broad academic qualifications. Micro-credentials offer a direct solution to this need, providing a clear signal of an individual’s proficiency in a particular area. This makes them incredibly attractive for both job seekers looking to enhance their marketability and employers aiming to fill critical skill gaps.
Defining Micro-Credentials in Today’s Context
Understanding what constitutes a micro-credential is key. They are distinct from traditional degrees in their scope and focus. Typically, they target a narrow set of skills, often digital or technical, and are awarded upon successful completion of a short course, project, or assessment.
- Focused Learning: Concentrated on a specific skill or competency.
- Verifiable: Often issued by reputable institutions or industry bodies, with clear assessment criteria.
- Flexible: Designed for adult learners, allowing for self-paced or blended learning.
- Stackable: Many micro-credentials can be combined to form larger qualifications.
Drivers Behind Their Growing Popularity
Several factors contribute to the escalating adoption of micro-credentials. The digital revolution has accelerated the obsolescence of certain skills while simultaneously creating demand for new ones. Traditional educational institutions often struggle to adapt quickly enough to these changes.
Furthermore, the rising cost of higher education and the desire for more agile career pathways have made micro-credentials an appealing alternative. They offer a more accessible and affordable route to gaining relevant skills without the long-term commitment of a degree program.
The emergence of micro-credentials is not merely a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how education and professional development are perceived and delivered. Their ability to deliver targeted, job-relevant skills quickly positions them as a cornerstone of future workforce strategies.
Bridging the Skill Gap: Micro-Credentials as a Strategic Solution
The US job market in 2025 faces a persistent and widening skill gap. Industries from technology to healthcare are struggling to find candidates with the specific expertise needed to drive innovation and maintain competitiveness. Micro-credentials are emerging as a powerful tool to address this critical challenge.
By offering specialized training in high-demand areas, micro-credentials allow individuals to quickly acquire the competencies employers are actively seeking. This agile approach to skill development is far more responsive than traditional academic pathways, which often take years to adapt to new industry requirements.
Identifying Critical Skill Shortages
Research consistently highlights key areas where skill shortages are most acute. These often include:
- Digital Literacy and Cybersecurity: Essential for nearly every sector.
- Data Analytics and AI: Driving decision-making and innovation.
- Cloud Computing: Fundamental to modern IT infrastructure.
- Project Management: Crucial for efficient execution in complex environments.
Micro-credentials directly target these areas, providing focused training that equips individuals with immediately applicable skills. This precision makes them an invaluable asset for both employees looking to upskill and employers needing to close talent gaps.
Employer Adoption and Recognition
A growing number of US employers are not only recognizing but actively seeking candidates with micro-credentials. Companies are beginning to integrate these certifications into their hiring processes and internal training programs. This shift reflects a pragmatic approach to talent acquisition, prioritizing proven skills over traditional academic credentials alone.
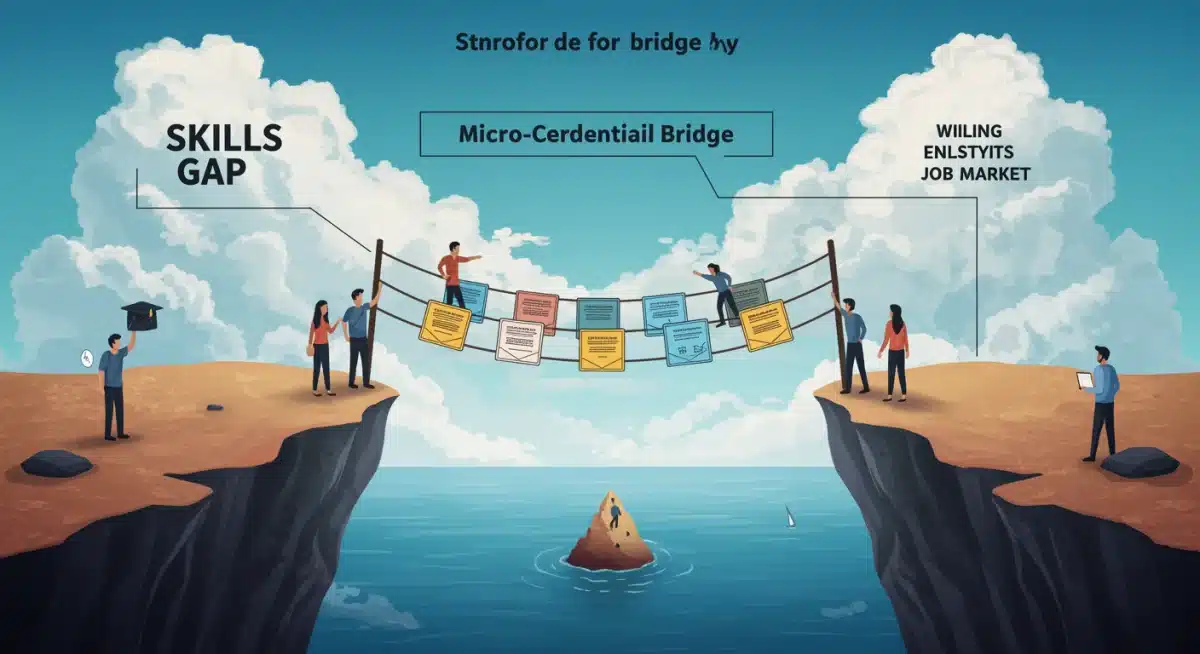
Furthermore, many organizations are partnering with educational providers to co-create micro-credential programs tailored to their specific needs. This collaborative effort ensures that the skills taught are directly relevant to industry demands, further enhancing the value and recognition of these qualifications.
Ultimately, micro-credentials are not just filling gaps; they are reshaping the very definition of a qualified candidate, making skills-based hiring a more prominent feature of the 2025 US job market.
Career Advancement and Upskilling Opportunities
For individuals navigating the complexities of the modern workforce, micro-credentials offer unparalleled opportunities for career advancement and continuous upskilling. They provide a flexible and efficient pathway to acquiring new competencies, making it easier to adapt to evolving job roles and industry demands.
Unlike lengthy degree programs that require significant time and financial investment, micro-credentials can be completed relatively quickly, allowing professionals to gain new skills without interrupting their careers. This agility is crucial in a job market that demands constant learning and adaptation.
Navigating Career Transitions with Micro-Credentials
Micro-credentials are particularly beneficial for individuals looking to pivot careers or move into new, high-growth sectors. By focusing on specific, in-demand skills, they provide a clear roadmap for acquiring the necessary expertise to enter a new field.
- Targeted Skill Acquisition: Learn exactly what’s needed for a new role.
- Reduced Time Commitment: Faster pathway to new career opportunities.
- Cost-Effective: More affordable than traditional retraining programs.
- Enhanced Marketability: Stand out to employers seeking specific proficiencies.
For example, an individual in traditional marketing might pursue micro-credentials in digital analytics or SEO to transition into a more specialized digital marketing role. This allows for a strategic and efficient career shift.
Lifelong Learning and Professional Development
The concept of lifelong learning has never been more relevant, and micro-credentials are at its forefront. They enable professionals to continuously update their skill sets, ensuring they remain competitive and relevant throughout their careers. This ongoing development is no longer a luxury but a necessity.
Employers are also recognizing the value of investing in micro-credential programs for their existing workforce. By providing access to these targeted learning opportunities, companies can foster a culture of continuous improvement, retain top talent, and ensure their teams possess the most current skills.
The flexibility and focus of micro-credentials make them an indispensable tool for both individual career growth and organizational workforce development, driving a more skilled and adaptable labor force in 2025.
The Economic Impact: Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
The economic implications of micro-credentials are profound, particularly in the context of cost-effectiveness and accessibility. As higher education costs continue to escalate, micro-credentials present a more affordable and often equally impactful alternative for skill development, especially for the US workforce.
This affordability opens doors for many individuals who might otherwise be excluded from advanced training due to financial barriers. It democratizes access to specialized knowledge and high-demand skills, fostering a more equitable and skilled labor market.
Reducing the Financial Burden of Education
Traditional degree programs, particularly at the postgraduate level, can incur substantial debt. Micro-credentials, conversely, typically involve a fraction of the cost, making them a financially viable option for upskilling or reskilling.
- Lower Tuition Fees: Significantly less expensive than full degrees.
- Shorter Duration: Less time out of the workforce, reducing opportunity costs.
- Targeted Investment: Pay only for the specific skills you need.
This cost efficiency means individuals can invest in their education more frequently and strategically, acquiring new skills as market demands evolve without accumulating crippling debt.
Expanding Access to Quality Training
Beyond cost, micro-credentials enhance accessibility in several ways. Many programs are offered online, removing geographical barriers and allowing individuals from rural areas or those with limited mobility to participate. The flexible scheduling often associated with these programs also caters to working professionals and caregivers.
This expanded access is crucial for building a diverse and inclusive workforce. It allows a broader spectrum of the population to gain the skills needed for well-paying jobs, contributing to economic growth and reducing income inequality.
Ultimately, the economic model of micro-credentials supports a more responsive and inclusive approach to workforce development, ensuring that valuable skills are within reach for a greater number of Americans in 2025.
Challenges and Opportunities for Widespread Adoption
While the benefits of micro-credentials are clear, their widespread adoption in the US job market by 2025 is not without its challenges. Overcoming these hurdles will be crucial for them to truly revolutionize professional development and hiring practices.
One significant challenge lies in standardization and recognition. With a multitude of providers offering various micro-credentials, ensuring quality and consistent recognition across industries remains a key concern. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration.
Ensuring Quality and Standardization
The unregulated nature of some micro-credential providers can lead to inconsistencies in quality. Employers need assurance that a micro-credential from one institution holds the same value and certifies the same level of proficiency as a similar one from another. This calls for greater industry involvement in defining standards and accreditation processes.
- Industry Collaboration: Employers and educators must work together to define relevant standards.
- Accreditation Bodies: The development of robust accreditation systems for micro-credentials.
- Clear Learning Outcomes: Programs should clearly articulate the skills acquired.
Efforts are underway by educational consortia and government bodies to establish frameworks for quality assurance, which will be vital for building trust and widespread acceptance.
Integration with Traditional Education and HR Systems
Another challenge is the seamless integration of micro-credentials into existing educational and human resources systems. For them to be truly impactful, they need to be easily recognized, tracked, and validated by academic institutions for credit transfer and by employers for hiring and promotion.
Opportunities exist in developing digital platforms and blockchain technologies that can securely store and verify micro-credentials, making them easily accessible and transferable. This would streamline the hiring process and allow individuals to build comprehensive digital skill portfolios.
By addressing these challenges through collaborative efforts and technological innovation, micro-credentials can solidify their position as a transformative force in the 2025 US job market, unlocking their full potential for both individuals and the economy.
The Future Outlook: Micro-Credentials as a Cornerstone
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, micro-credentials are poised to become a fundamental component of the US job market’s educational and hiring ecosystem. Their adaptability, affordability, and focus on immediate skill application make them indispensable for a dynamic and rapidly evolving economy.
The trajectory suggests that these targeted certifications will not merely supplement traditional degrees but will increasingly stand on their own as valid and highly sought-after qualifications. This shift will empower individuals to take more control over their learning pathways and career trajectories.
Personalized Learning Pathways
One of the most exciting aspects of the future of micro-credentials is their potential to enable highly personalized learning pathways. Individuals will be able to curate their own educational journeys, selecting specific micro-credentials that align with their career goals and the demands of the job market.
- Customized Skill Stacks: Build unique profiles of in-demand competencies.
- Agile Skill Development: Adapt to new industry trends with speed.
- Continuous Growth: Maintain relevance throughout a professional career.
This individualized approach moves away from a one-size-fits-all model of education, fostering a more engaged and empowered learner.
Impact on Corporate Training and Development
Corporations will increasingly leverage micro-credentials for internal training and development programs. Instead of generic workshops, companies can implement highly targeted micro-credential programs to upskill their workforce in specific areas like AI ethics, advanced data visualization, or sustainable business practices.
This not only ensures that employees have the most current skills but also demonstrates a commitment to their professional growth, aiding in retention and talent attraction. The investment in micro-credentials will be seen as a strategic advantage for businesses aiming to remain competitive.
In essence, the future outlook for micro-credentials in the US job market is bright. They are set to become a cornerstone of lifelong learning, personalized career development, and responsive corporate training, shaping a more skilled, adaptable, and resilient workforce for 2025 and beyond.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Skill Gap Solution | Micro-credentials offer targeted training to quickly close critical skill shortages in the US job market. |
| Career Advancement | They provide flexible, efficient pathways for upskilling and career transitions for individuals. |
| Economic Accessibility | More affordable than traditional degrees, expanding access to quality training across diverse populations. |
| Future Cornerstone | Expected to be a fundamental part of personalized learning and corporate training by 2025. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Micro-Credentials
A micro-credential is a certification of specific, verifiable skills or competencies acquired through a focused, short-term learning experience. Unlike traditional degrees, they target narrow areas of expertise and are often digitally-verifiable, making them highly relevant for immediate job market needs.
For job seekers, micro-credentials offer a fast, affordable way to gain in-demand skills, bridge personal skill gaps, and enhance marketability. They enable quicker career transitions and provide tangible proof of proficiency to potential employers, boosting employability in a competitive landscape.
Yes, a growing number of US employers are increasingly recognizing and valuing micro-credentials. Many companies are integrating these certifications into their hiring processes and internal training programs, viewing them as a reliable indicator of specialized skills directly applicable to critical roles and projects.
Key challenges include ensuring consistent quality and standardization across diverse providers, as well as integrating them seamlessly into existing education and HR systems. Overcoming these requires collaboration between educators, industry, and technology developers to build trust and facilitate recognition.
While micro-credentials are gaining significant traction, they are unlikely to fully replace traditional degrees by 2025. Instead, they will increasingly complement degrees, offering specialized skill sets and continuous learning opportunities, creating a more diversified and flexible educational ecosystem for career development.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored, the role of micro-credentials in the 2025 US job market is not merely supplementary; it’s transformative. These agile, focused certifications are actively reshaping how skills are acquired, validated, and valued, offering a powerful solution to the persistent skill gap and providing individuals with flexible pathways for career advancement. Their cost-effectiveness and accessibility are democratizing specialized training, making high-demand skills attainable for a broader segment of the workforce. While challenges in standardization and integration remain, the future outlook suggests micro-credentials will become a cornerstone of personalized learning and corporate development, fostering a more skilled, adaptable, and resilient American workforce ready for the challenges and opportunities of tomorrow.